Sterility Testing of Products with Antimicrobial Properties
Sterility Testing of Antibiotics and Products with Inhibitory Properties
Some pharmaceutical drugs are formulated with antibiotics, preservatives, or other chemicals that affect microbial viability and growth. When these drugs are tested for sterility, it is necessary to eliminate their inhibitory effects. If not, the recovery of the microorganisms present in the sample may be reduced, thereby increasing the risk of a false negative result. As described in the pharmacopeias (Ph. Eur 2.6.1, USP <71> and JP 4.06), membrane filtration is the method of choice for sterility testing, whenever the nature of the products permits. To be effective against antimicrobial effects, filtration must be combined with adapted systems and appropriate procedures.

Figure 1.Steritest® NEO membrane filtration device.
We recommend following three golden rules to prevent false negative results:
- Maximize the solubility of the antimicrobial agent
- Minimize the contact time with the membrane
- Optimize the membrane rinsing
- Related Products
The “Red Base” Steritest® NEO devices incorporated with 0.45 μm Durapore® membrane provides low antibiotic binding, which improves rinsing efficiency and reduces the risk of false negative results.
Sterility Testing Requirements: Materials and Equipment
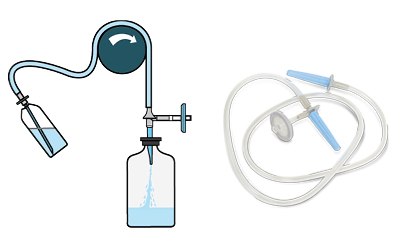
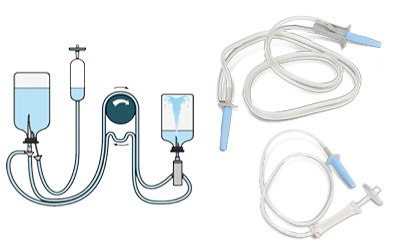
Figure 2.Sterility testing set up of Steritest® NEO device for antibodies.
- Steridilutor® NEO device with expansion chamber: TZVC00010
- Steridilutor® NEO device for liquid transfer kit: TZA000010
- Red base Steritest® NEO filtration devices: TZHVAB210 or TZHVAB205 (double packed) Soybean–casein digest medium (SCDB), fluid thioglycollate medium (FTM), clear fluid thioglycollate medium (CTM)
- Rinsing fluid A, fluid D, fluid K: double packaged media and fluids available in different formats
- Steritest® Symbio Pump for laminar flow hood or isolator
Maximize the solubility of antimicrobial agent: Dissolve and/or dilute the product
Pure solid or liquid products are difficult to rinse and residues from products might considerably inhibit sterility testing. Powders, on the other hand, should be dissolved completely to avoid the formation of aggregates as membranes show a great affinity for aggregates. For liquid antibiotics, a dilution step is strongly recommended to reduce the concentration of the antimicrobial agent. This will reduce the possibility of agent binding to the filter.
Specific Steritest® NEO closed systems allow aseptic dissolution/dilution of product samples. The Steridilutor® NEO system is specifically designed to dissolve and dilute drugs in vials. The Steridilutor® NEO device for liquid transfer kit allows liquid dilution from open ampoules into a diluent container with a septum.
Minimize the contact time with the membrane
Molecule adsorption onto a membrane surface depends on its polymeric structure. For sterility testing of the antibiotics or products with preservatives, USP recommends a “low binding filter material, such as polyvinylidene difluoride” (USP33, chapter <1227>). Another important factor to consider is the thickness of the membrane. The thinner the membrane, the lower the risk of retention will be during filtration, as inhibitory residues can be trapped within the membrane.
Steridilutor® NEO system devices for antibiotics and products with antimicrobial activity are specifically designed for this application. These devices are made from low-binding PVDF filter material (Durapore®) which has a thin membrane of about 120 to 150 μm. If multiple samples need to be filtered it is recommended to pool them before filtration. The Steridilutor® NEO device pools liquid into one single container without the risk of cross-contamination. Filtration of the pooled samples is carried out at once by using the red base Steritest® NEO filtration device (TZHVAB210).
Note: TZHVAB210 unit, among the red base filtration devices, is always recommended for testing antibiotics.
Optimize the membrane rinsing: Use a test device configuration that minimizes product retention
The way a closed sterility test device is assembled can increase the risk of false negative results. In some filtration devices available in the market, the membrane is held in place by pinching it between the edge of the filtration canister and the base of the device. This design generates “pockets” at the periphery of the membrane which collect residues during product filtration. Removal of these residues by rinsing is difficult and often impossible. With Steritest® NEO devices, the membrane is thermosealed to a specific holder (base), without generating edge “pockets”. Trapping of product residues is therefore prevented, optimizing rinsing efficacy.
Discover our full range of products for sterility testing by visiting our webpage.
Method Development and Validation Services
Our team of experienced and trained engineers will assist you in implementing method development and validation protocol within your QC microbiology lab. Additionally, you will be provided with basic and advanced technical training on your installed equipment, on-site or remotely.
Rely on our expertise to support you in various situations including:
- New laboratory sterility testing equipment
- New product or reformulated product sterility testing
- Compliance with updated regulations: EP, USP, JP, etc.
- PQ consultancy after the completion of IQ/OQ
- Method development execution or consultancy
- Investigation of out-of-specification results
Related Products
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?