Middle-Up Antibody Analysis by RP Chromatography
Section Overview
INTRODUCTION
Analysis of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is a difficult analytical challenge that requires a multi-pronged approach. Different modes of chromatography, in addition to different sample preparation strategies, need to be employed for complete characterization. In reversed-phase mode, three levels of analysis are typically performed: top-down (intact), bottom-up (fully digested peptide fragments), and middle-up (larger protein sub-units).
In middle-up analysis, a digestion procedure, such as using dithiothreitol (DTT) or IdeS (a protease) is employed to break the protein into larger fragments. DTT breaks a mAb down into a light chain (LC) fragment and a heavy chain (HC) fragment; IdeS breaks the mAb down into a fragment crystallizable (Fc) fragment and an antigen-binding fragment (Fab). These two approaches lead to a simpler mixture than a full tryptic digest which enables easier identification of variants.
The purpose of this application is to subject the SigmaMAb antibody reference standard and the NISTmAb reference standard to DTT and IdeS digestion and analyze each of the resulting digests by RPC. In addition, a series of columns will be employed to perform the analysis, and the differences in selectivity, efficiency, and peak shape will be examined.
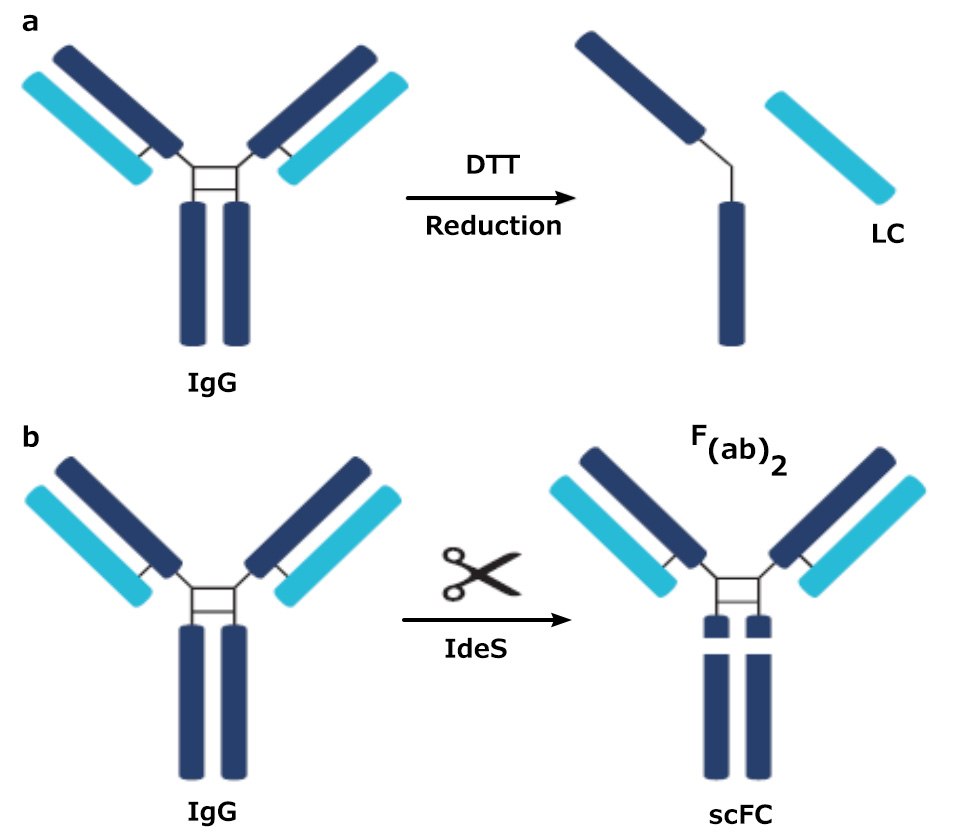
Figure 1.Digested products of an IgG antibody after being subjected to a) DTT and b) IdeS
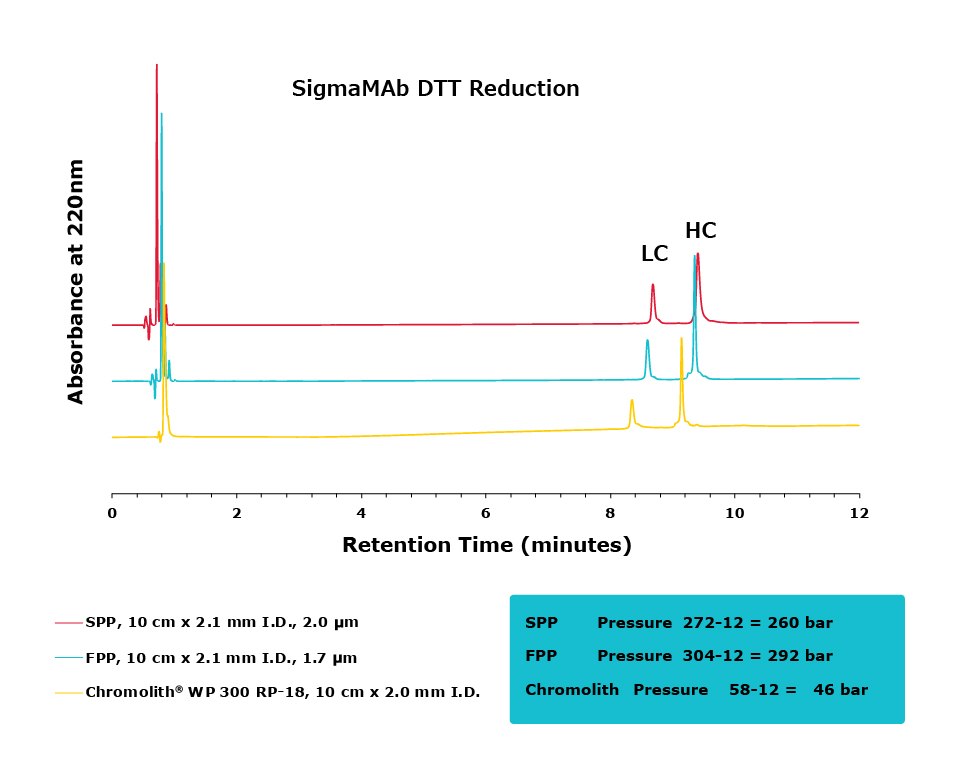
Figure 2.Comparison of separation performance between Chromolith® WP 300, a SPP, and an FPP-packed column analyzing DTT reduced SigmaMAb. Chromolith® performs comparably to these UHPLC columns but with reduced backpressure.
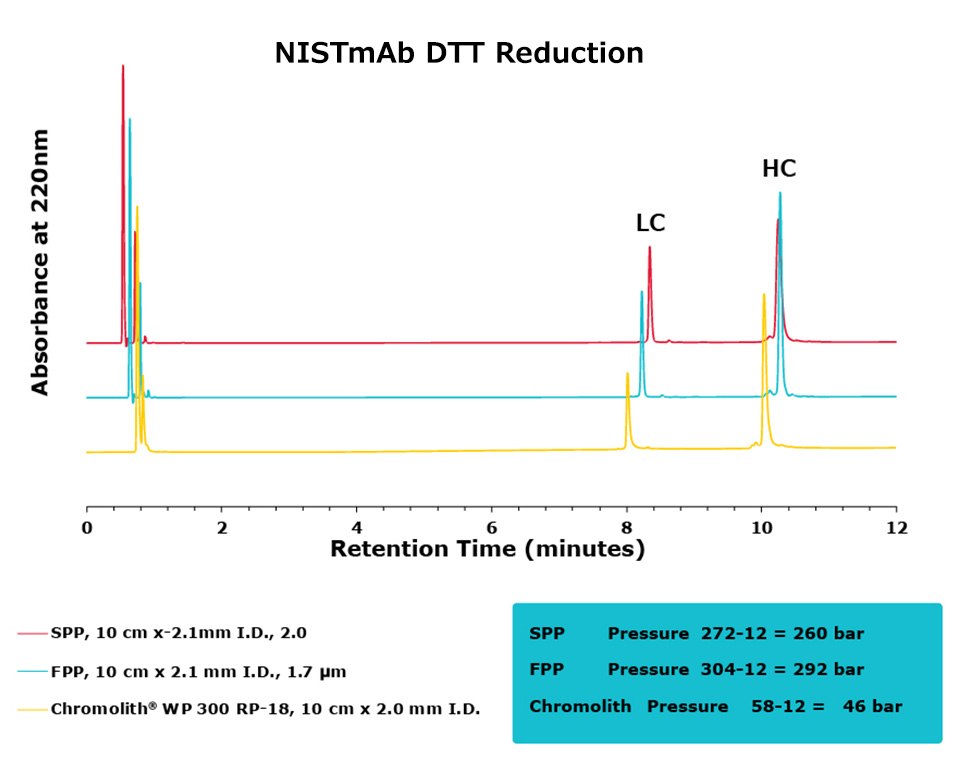
Figure 3.Comparison of separation performance between Chromolith®, a SPP, and an FPP-packed column in analyzing DTT reduced NISTmAb. Chromolith® performs comparably to the UHPLC columns but at a significantly lower backpressure.
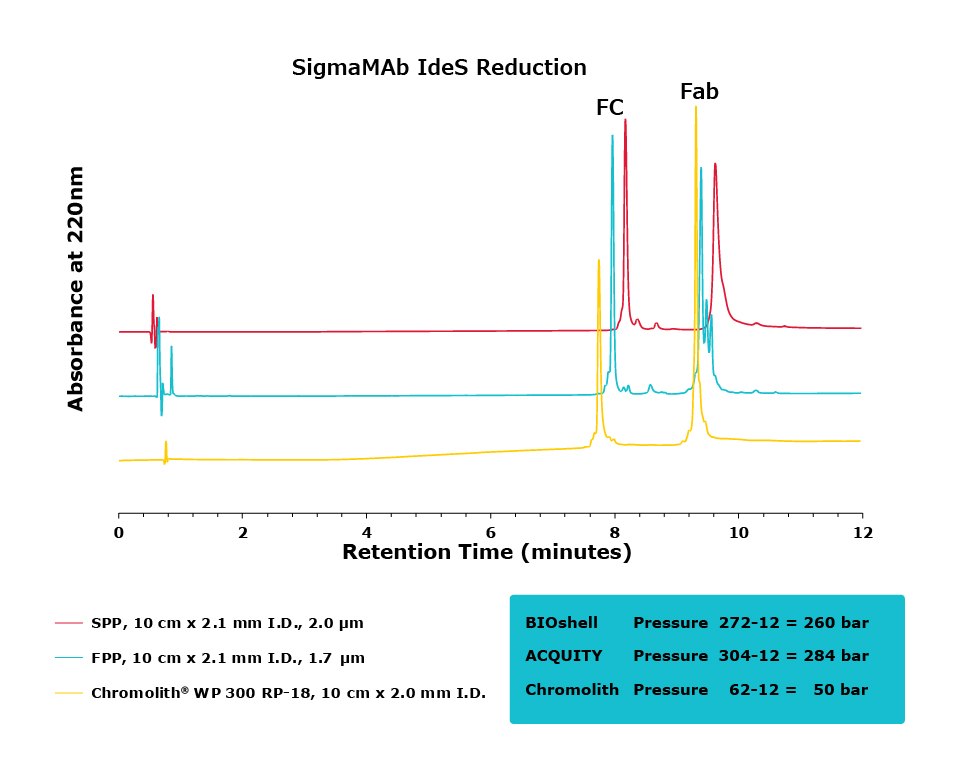
Figure 4.Comparison of separation performance between Chromolith®, a SPP, and an FPP-packed column in analyzing IdeS reduced SigmaMAb. Chromolith® is able to separate the Fab and Fc species with high resolution without generating artifacts due to higher pressure, as illustrated by extra peaks and peak broadening in the FPP and SPP, respectively.
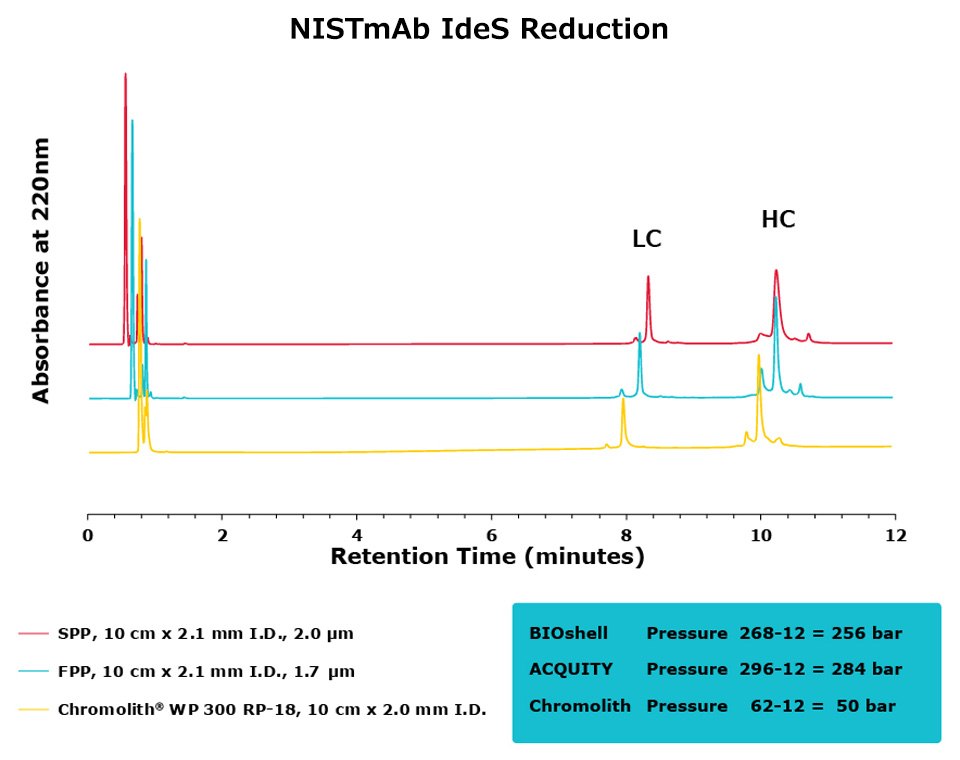
Figure 5.Comparison of separation performance between Chromolith®, a SPP, and an FPP-packed column in analyzing IdeS digested NISTmAb. The Chromolith® column performs just as well as the UHPLC columns.
CONCLUSION
The purpose of this study was to compare the performance of a series of columns in resolving medium-sized fragments of antibodies, after digestion, by RPC. Two different digestion protocols were employed in this study, DTT and IdeS. All three columns achieved excellent resolution between the two protein subunits. For the DTT digest, the Chromolith® WP 300, 2 mm I.D. column achieved equivalent UHPLC performance to the two, dedicated UHPLC columns, indicating that it has equivalent separating performance. As an added benefit, this performance was achieved at ~16% the pressure drop of the FPP column.
For the IdeS digestion, the Chromolith® WP 300, 2 mm I.D. column exhibited better separation performance than the SPP column, as is illustrated by the improved resolution of variants around the Fab peak in both SigmaMAb and NISTmAb. In what appears to be peak splitting occurring on the Fab peak of SigmaMAb on the FPP is actually a new variant generated from the high backpressure seen on the FPP. This artifact is mitigated, without a compromise in efficiency, on the Chromolith® WP 300, 2 mm I.D. column. Further research will examine the composition of this variant.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?