Purification of Histidine-Tagged Proteins using HiTrap® IMAC HP and HiTrap® IMAC FF
HiTrap® IMAC HP and HiTrap® IMAC FF are 1 ml and 5 ml columns prepacked with IMAC Sepharose® High Performance or IMAC Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow, respectively. Sample application, washing, and elution can be performed using a syringe with a supplied adapter, a peristaltic pump, or a liquid chromatography system such as ÄKTA.
HiTrap® IMAC HP and HiTrap® IMAC FF columns are made of polypropylene, which is biocompatible and noninteractive with biomolecules. The top and bottom frits are manufactured from porous polyethylene. Columns are delivered with a stopper on the inlet and a snap-off end on the outlet. Each package includes all necessary components for connecting the columns to different types of equipment. For quick scale-up of purifications, two or three HiTrap™ columns (1 ml or 5 ml) can be connected in series (back pressure will be higher). Note that HiTrap™ IMAC columns cannot be opened or refilled.

Figure 3.49.HiTrap™ IMAC HP 1 ml columns charged with Cu2+, Zn2+, Co2+ and Ni2+, respectively.
Sample and buffer preparation
Refer to Purification using IMAC Sepharose® High Performance or Purification using IMAC Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow for a general procedure for sample and buffer preparation, for HiTrap™ IMAC HP and HiTrap™ IMAC FF, respectively.
Charging the column with metal ion
- Prepare a 0.1 M solution of the desired metal ion (e. g., Cu2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Fe3+, or Ni2+) in distilled water. Salts of chlorides, sulfates, etc., can be used (e.g., 0.1 M CuSO4 or 0.1 M NiSO4).
Solutions of Zn2+ ions should have a pH of approximately 5.5 or lower to avoid solubility problems that arise at pH 6 or higher. Fe3+ ions should be immobilized at low pH (approximately pH 3.0) to avoid formation of insoluble ferric compounds.
- Fill the pump tubing or syringe with distilled water. Remove the stopper and connect the column to the chromatography system tubing, syringe (use the connector supplied), or laboratory pump “drop to drop” to avoid introducing air into the system.
- Remove the snap-off end at the column outlet.
- Wash out the ethanol with 5 ml (HiTrap™ IMAC HP or FF 1 ml columns) or 15 ml (HiTrap™ IMAC HP or FF 5 ml columns) of distilled water. Do not use buffer to wash the column at this stage; a buffer wash may cause the metal ion to precipitate during step 5.
- Charge the water-washed column by loading at least 0.5 ml (HiTrap™ IMAC HP or FF 1 ml columns) or 2.5 ml (HiTrap™ IMAC HP or FF 5 ml columns) of 0.1 M metal ion/salt solution.
- Repeat the water wash described in step 4.
- Equilibrate the column with at least 5 column volumes of binding buffer. Recommended flow rates are 1 ml/min or 5 ml/min for the 1 ml and 5 ml columns, respectively.
Wash only with water, not buffer, prior to applying the metal ion solution, otherwise unwanted precipitation may occur.
The column does not need to be stripped and recharged between each purification if the same protein is going to be purified. Reuse of any purification column depends on the nature of the sample and should only be performed with identical tagged proteins to prevent cross-contamination. For more information on this topic and on cleaning and storage, refer to Appendix 1 (Characteristics of Ni Sepharose, Ni Sepharose® excel, TALON® Superflow, and uncharged IMAC Sepharose® products).
IMAC Sepharose® is compatible with reducing agents. However, we recommend removal of any weakly bound metal ions before applying buffer/sample that includes reducing agents. This can be accomplished by performing a blank run without reducing agents (see below). Do not leave or store HiTrap™ IMAC columns with buffers that include reducing agents.
For critical applications, leakage of metal ions during purification can be diminished by performing a blank run (as described on the next page) before loading sample.
Blank run:
Use binding buffer and elution buffer without reducing agents.
- Wash the column with 5 column volumes of distilled water (to remove the 20% ethanol).
- Wash with 5 column volumes of elution buffer.
- Equilibrate with 10 column volumes of binding buffer.
Purification
- Apply the pretreated sample using a syringe fitted to the connector or by pumping it onto the column. For best results, use a flow rate of 0.2 to 1 ml/min (1 ml column) and 0.5 to 5 ml/min (5 ml column) during sample application1.
- Wash with binding buffer (generally at least 10 to 15 column volumes) until the absorbance reaches a steady baseline.
- Elute with elution buffer using a one-step or linear gradient. For step elution, 5 column volumes usually suffice. A linear gradient over 20 column volumes or more may separate proteins with similar binding strengths.
- After elution, regenerate the column by washing it with 5 to 10 column volumes of binding buffer. The column is now ready for a new purification.
1 One ml/min corresponds to approximately 30 drops/min when using a syringe with a HiTrap™ 1 ml column, and 5 ml/min corresponds to approximately 120 drops/min when using a HiTrap™ 5 ml column.
The column does not need to be stripped and recharged between each purification if the same protein is going to be purified. Reuse of any purification column depends on the nature of the sample and should only be performed with identical tagged proteins to prevent cross-contamination. For more information on this topic and on cleaning and storage, refer to Appendix 1 (Characteristics of Ni Sepharose, Ni Sepharose® excel, TALON® Superflow, and uncharged IMAC Sepharose® products).
Application example
Purification screening using different metal ions
YNR064c (Mr 33 700) is a (histidine)6-tagged protein expressed in Pichia pastoris. It was purified using HiTrap IMAC HP 1 ml columns charged separately with Cu2+, Zn2+, Co2+, or Ni2+; conditions were otherwise the same for the four purifications. See Figures 3.50A–E for the resulting chromatograms and SDS-PAGE analysis of pooled fractions.
The results show that for this (histidine)6-tagged target protein, the highest purity was achieved with Ni2+ or Cu2+, although Cu2+, at the conditions used, apparently gave a small loss of target protein (Figure 3.50E, lane 4).
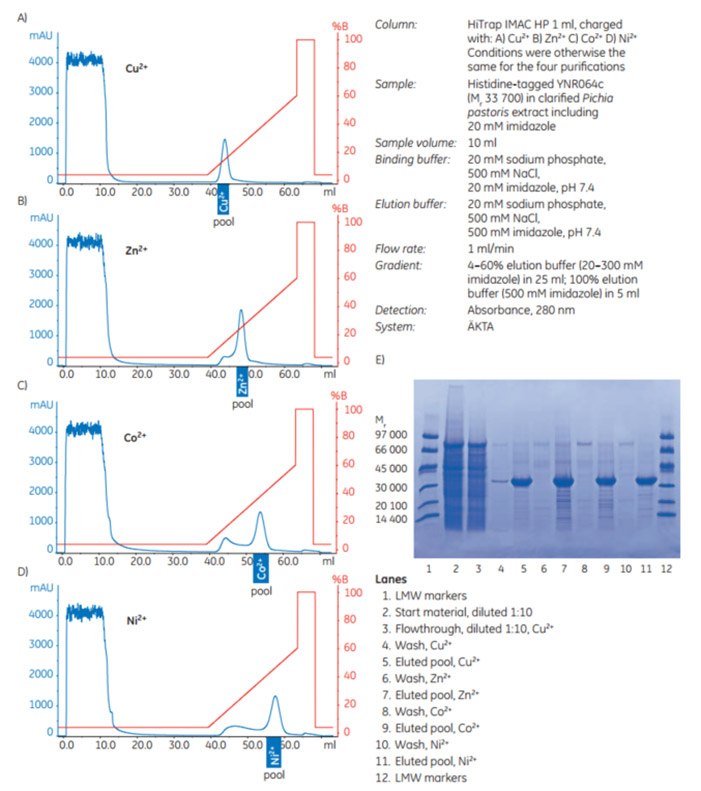
Figure 3.50.Purification of (histidine)6-tagged YNR064c expressed in Pichia pastoris on four different HiTrap IMAC HP 1 ml columns charged separately with metal ions (A) Cu2+, (B) Zn2+, (C) Co2+, or (D) Ni2+. Pools selected after SDS-PAGE of individual 1 ml fractions (not shown) are indicated. (E) SDS-PAGE analysis: reducing conditions on ExcelGel SDS Gradient 8–18; Coomassie staining.
Materials
Materials
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?