Magnetic Bead-Based Purification/Screening Using His Mag Sepharose® Ni
His Mag Sepharose® Ni is a magnetic-bead-based IMAC medium charged with nickel ions. It is designed for efficient, small-scale purification/screening of histidine-tagged proteins from various sources. Histidine-tagged proteins are captured using immobilized nickel ions followed by collection of the beads using a magnetic device. For purification of histidine-tagged proteins secreted into eukaryotic cell culture medium it is recommended to use His Mag Sepharose® excel.
A vial containing 1 mL of 5% medium slurry is sufficient for five purification runs according to the recommended protocol. Together with MagRack 6, a separation tool for handling the beads in microcentrifuge tubes, up to six samples can be processed in parallel. A larger magnetic rack, MagRack Maxi, can be used for capture of low-expressed histidine-tagged proteins in sample volumes up to 50 mL. For screening of a larger number of samples in parallel with high throughput, a robotic device can be used.
Figure 3.28.His Mag Sepharose® Ni for small-scale purification/screening. His Mag Sepharose® Ni is available as a 5% medium slurry in 2 × 1 mL, 5 × 1 mL, and 10 × 1 mL pack sizes.
General Magnetic Separation Steps
When performing magnetic separation, it is recommended to use MagRack 6 for test tubes up to 1.5 mL and MagRack Maxi for test tubes up to 50 mL
- Remove the magnet before adding liquid.

- Insert the magnet before removing liquid.
When using volumes above 50 mL, the beads can be spun down using a swing-out centrifuge.
Dispensing the Medium Slurry
- Prior to dispensing the medium slurry, make sure it is homogeneous by vortexing the vial thoroughly.
- When the medium slurry is resuspended, immediately pipette the required amount of medium slurry into the desired tube.
- Due to the fast sedimentation of the beads, it is important to repeat the resuspension between each pipetting.
Handling Liquids
- Before application of liquid, remove the magnet from the magnetic rack.
- After addition of liquid, resuspend the beads by vortexing or manual inversion of the tube. When processing multiple samples, manual inversion of the magnetic rack is recommended.
- Use the magnetic rack with the magnet in place for each liquid removal step. Pipette or pour off the liquid. If needed, a pipette can be used to remove liquid from the lid of the test tube.
Incubation
During incubation, make sure the magnetic beads are well resuspended and kept in solution by end-over-end mixing or by using a benchtop shaker.
Incubation generally takes place at room temperature. However, incubation can take place at 4 °C if this is the recommended condition for the specific sample.
When purifying samples of large volumes, an increase of the incubation time may be necessary.
Sample and Buffer Preparation
Refer to Purification using Ni Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow earlier in this chapter for a general procedure for sample and buffer preparation.
Suitable buffers can be easily prepared using His Buffer Kit.
Insufficient lysis may require clarification of sample before applying it to the beads.
Purification
Magnetic bead preparation
- Mix the bead slurry thoroughly by vortexing. Dispense 200 µL of homogeneous slurry into a 1.5 ml test tube.
- Place the test tube in the magnetic rack.
- Remove the storage solution.
Equilibration
- Add 500 µL of binding buffer.
- Resuspend the beads.
- Remove the liquid.
Sample Application
- Immediately after equilibration, add 1000 µL of sample. If the sample volume is less than 1000 µL, dilute to 1000 µL with binding buffer.
- Resuspend the medium and incubate for 30 min with slow end-over-end mixing or by using a benchtop shaker.
- Remove the liquid.
Washing (perform this step 3 times in total)
- Add 500 µL of binding buffer.
- Resuspend the beads.
- Remove the liquid.
Elution
- Add 100 µL of elution buffer.
- Resuspend the beads.
- Remove and collect the elution fraction. The collected elution fraction contains the main part of the purified protein. If desired, repeat the elution.
Application Example
Purification of a cell-wall-associated protein in Lactococcus lactis
A histidine-tagged cell-wall-associated protein from Staphylococcus aureus was expressed in Lactococcus lactis and purified using His Mag Sepharose® Ni. The primary goal was to obtain high purity, therefore 50 mM imidazole was included in the sample and binding buffer. The SDS-polyacrylamide gel shows a minor leakage of target protein during sample application and wash, as a result of the relatively high imidazole concentration. The purity of the eluted target protein was above 95%, and the yield was approximately 600 µg of purified protein (Figure 3.29).
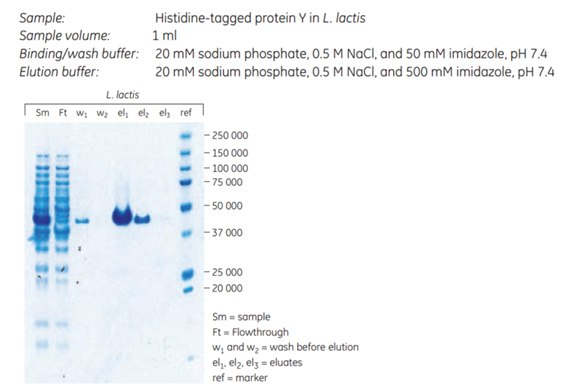
Figure 3.29.Purification of a cell wall protein in L. lactis resulted in high purity (> 95%) according to SDS-polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie.
Acknowledgement
The results for histidine-tagged protein purification in L. Lactis were kindly provided by Prof. Jan-Maarten van Dijl and Dennis Koedijk, University Medical Centre of Groningen (UMCG), Groningen, The Netherlands.
Materials
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?