Willis Pyridinates for Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions
Introduction
The Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction is one of the most used transformations in the pharmaceutical industry to form carbon-carbon bonds.1,2 However, limitations to the application of this reaction in discovery chemistry persist, including the notorious low reaction efficiency, poor stability, and difficulty in preparing pyridine-2-boronates and boronic acids for cross-coupling.
Read more about
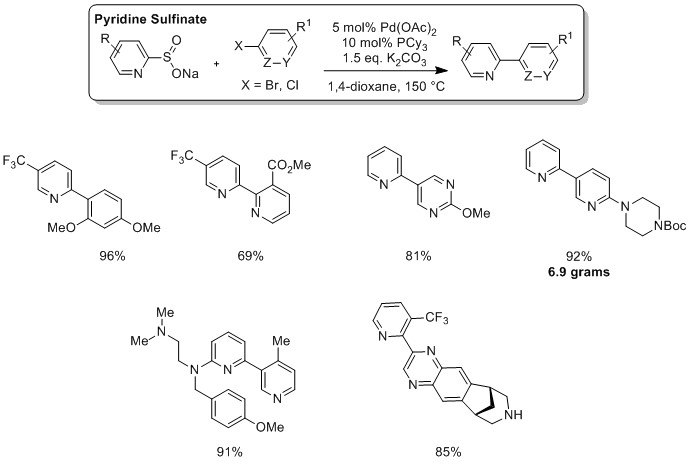
Professor Willis and industrial partners at Pfizer have shown that by replacing boronates with pyridine-2-sulfinates as nucleophilic coupling partners, a palladium-catalyzed desulfinylative cross-coupling process of exceptional scope can be realized.3 Both aryl bromides and aryl chlorides can be employed as coupling partners to access challenging and medicinally relevant linked pyridine-heterocycle building blocks.

Advantages
- Bench-stable, solid reagents
- Efficient nucleophilic cross-coupling partners
- Convenient removal during aqueous work-up
Special thanks to Tim Markovic and Prof. Michael Willis for contributing this Technology Spotlight!
References
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?