Risk Considerations for the Presence of Pyrogens and the Need for the MAT Test in Pharmaceutical Processing
WEBINAR
Pyrogens can cause severe reactions such as fever, rash, headache or toxic shock to the recipient. To minimize the risks from these sources, FDA and EMA recommend good control of the microbiological and endotoxin levels of contamination in the potential source. In this lecture, you will learn how to test for pyrogen (including non-endotoxin pyrogens) in your pharmaceutical samples, what are the existing methods in order to have a controlled process.
Speakers

Tim Sandle
University of College London & University of Manchester
Head of Microbiology at BPL and visiting tutor
Question & Answer Themes
- Pyrogen and Endotoxin Tests
- Regulatory Landscape and Guidelines
- MAT in Practice
Pyrogen and Endotoxin Tests
I am interested in MAT since we are more and more sensitive about animal welfare. How robust do you think this method is to replace rabbit testing?
Generally speaking, the Rabbit Pyrogen Test is known to have quite a low robustness. Robustness is known as the ability of a method to remain unaffected when slight variations are applied. This is difficult to achieve with animal-based tests, knowing that rabbits are often affected by stress during testing, which can impact the test results.
Here is a comparison of key parameters of the two methods:
How do you see MAT and LAL live together, will they be complementary or at some point MAT might replace LAL testing?
Would you advise MAT as a routine test in process or rather a solution for release testing on the final product?
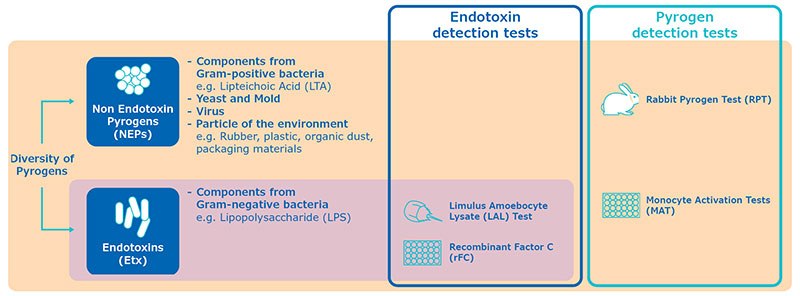
Due to its high sensitivity for endotoxin detection, its low cost and short time to result, Bacterial endotoxin test (using LAL or rFC) is an interesting choice for in process testing to monitor the contamination along the production process. It is also very practical for screening water, which is a raw material where the risk for endotoxin contamination is known to be quite high.
For a safe batch release, a pyrogen test should be preferred to avoid missing out on non-endotoxin pyrogens in the final drug product. Monocyte Activation Test, based on human model and with a high sensitivity is a good option for batch release.
How do MAT tests differ from rFC LAL in terms of the specificity mentioned (non-endotoxin pyrogens)?
Both the LAL and rFC tests are specific for endotoxin. They are really designed to quantify the concentration of LPS in a sample.
MAT will detect endotoxin but also primary components from Gram-positive bacteria or viral particles, known as non-endotoxin pyrogens.
MAT is using human monocytic cells – simulating cytokine reaction in the body when a pyrogen comes in contact with blood. It is designed to measure the pyrogenicity of a sample (expressed in endotoxin-equivalent units).
I hear a lot about rFC, also a non-animal based solution for endotoxin testing - is it faster than MAT?
What would you advise between the two?
It is important to distinguish the test methods based on their specificity: MAT and RPT are pyrogen tests, whereas rFC and LAL are endotoxin test.
Both LAL test and rFC test are faster than MAT as they give results within a few hours, however they will only give the quantification of endotoxins, whereas MAT will determine the pyrogenicity of the sample, including potential contamination from non-endotoxin pyrogens.
MAT gives results within 1.5 days as it requires incubating the sample with the monocytic cells for 20 to 24h to allow the release of cytokines.
How do you value the MAT market today, is it still under consolidation?
Do you foresee new suppliers coming in the next years?
The MAT market has evolved a lot in the last decade. The first ready-to-use solution was commercialized in 2010. Then new players entered the market and additional kits were commercialized starting from 2017. There are now 7 commercial solutions available on the market showing a very promising trend.
Regulatory Landscape and Guidelines
The regulatory landscape is slowly evolving, MAT being consider as an alternative method in the US - do you think that ultimately US, China and Japan will follow the same path and approve it as compendial method?
In terms of regulations, now that many ready to use kits are on the market do you think that MAT will become a compendial method in the US?
As of today, MAT is mentioned in the US regulatory guidelines as follows:
The new version of USP <151> (Pyrogen test) mentions that: “A validated, equivalent in vitro pyrogen or bacterial endotoxin test may be used in place of the in vivo rabbit pyrogen test, where appropriate.” This has been effective since 1st May 2017.
In addition, MAT is addressed in the FDA “Guidance for Industry Pyrogen and Endotoxins Testing: Questions and Answers” as an example of alternative assay for pyrogen detection.
Whether MAT will become compendial in the US is still a question mark. An increasing need coming from the pharma industry and file submissions asking for the use of MAT as a release test would surely support the evaluation of the method for implementation in the USP as a compendial method.
Japan is also a key country when it comes to Quality Control regulatory guidelines. The JaCVAM experts are responsible for submitting alternative methods to animal testing to Japanese Pharmacopeia. There are currently ongoing evaluations and discussions around MAT.
Do you think that rabbit testing will be forbidden in Europe in the years to come?
What about the situation of Rabbit testing versus MAT?
For how long do you think animal testing will be accepted, and is MAT a valuable alternative?
The European Pharmacopeia, in line with Directive 2010/63/EU (Directive on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes) is recommending to replace the Rabbit Pyrogen Test by Monocyte Activation Test wherever possible as stated in the chapter 2.6.8.
In June 2021, the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) Commission took the decision to engage on a path that should ultimately lead to the complete replacement of the rabbit pyrogen test (RPT) in the Ph. Eur., within approximately 5 years. Read the article.
The Ph. Eur. is committed, for all the current 59 Ph. Eur. texts, to replacing the test for pyrogens with a suitable in-vitro alternative, ultimately leading to the complete elimination of the RPT. In the meantime, users are actively encouraged to seek alternatives to chapter 2.6.8, the best option being the MAT.
It is also interesting to note that in Germany an official letter was issued by German Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices & Paul Ehrlich Institute stating that the notifiable Rabbit Pyrogen Test at one of the major German contract laboratories would no longer be supported by the competent state authorities.
However, Rabbit Pyrogen Test will remain an option when other test methods are not suitable for the tested sample.
Does the regulatory bodies require labs to provide the risk assessment data on Pyrogen contamination using MAT test if they are using only LAL endotoxin test for product release?
From a personal experience (with FDA and EMA), a paper-based assessment would be ok. This risk assessment can, for example, include supporting bioburden data. Nevertheless, depending on the outcome of the risk assessment and concerns about NEPs, it may be necessary to provide results from MAT and LAL testing to support the decision of choosing one test method or another for release.
How many Non endotoxin Pyrogens should I use in my validation?
The European Pharmacopeia – Chapter 2.6.30 mentions that “the preparatory testing is to include validation of the system using at least 2 non-endotoxin ligands for toll-like receptors […] at least 1 of which is to be spiked into the preparation being examined. The choice of non-endotoxin pyrogens used should reflect the most likely contaminant(s) of the preparation being examined”.
MAT in Practice
Would you be able to give 1 example where MAT should be adopted for pyrogen testing (API or Drug product or vaccine)?
Based on the EP Chapter 2.6.8 (Pyrogen Test), it is recommended to replace RPT by MAT wherever possible and after product specific validation. So in theory, MAT should at least be evaluated for any drug currently tested with RPT. If MAT is shown to be suitable for the sample (no interference with the test method), it should then be adopted.
For products released with the LAL test, it depends on the product, the production process and the associated risk assessment. For example, some blood products are not easy to test with LAL test, MAT could help.
Would detection of viral particles then be a problem for virus-based products (vaccines?)
If vaccines have an inherent pyrogenicity linked to their composition that prevents endotoxin spike recovery then the Method C “reference lot comparison” can be used.
Microbiological testing
- Pyrogen testing
期间:24min
语言:English
场次 1:往期 June 16, 2021
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?