Hematopoietic Cytokines
Hematopoietic cytokines are large family of extracellular ligands that stimulate hematopoietic cells to differentiate into eight principle types of blood cells. Numerous cytokines are involved in the regulation of hematopoiesis within a complex network of positive and negative regulators. Some cytokines have very narrow lineage specificities of their actions, while many others have rather broad and overlapping specificity ranges.1
Listed within this section are the cytokines whose predominant action appears to be the stimulation or regulation of hematopoietic cells. This includes GM-CSF, G-CSF, M-CSF, interleukins, EPO and TPO. There are a number of other cytokines that exert profound effects on the formation and maturation of hematopoietic cells, which include stem cell factor (SCF), flt-3/flk-2 ligand (FL) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Other cytokines or ligands such as jagged-1, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) also play significant roles in modulating hematopoiesis.
Two models were proposed to define the role of growth factors in hematopoietic differentiation.
- Instructive model assigns a direct role to cytokines in cell differentiation; cell fate is determined predominantly by the type of growth factor acting on the cell2
- Stochastic model suggests a pre-determined program for cell differentiation; growth factors are required specifically for survival and proliferation of committed progenitor cells3
Both models are based on evidence that growth factors control survival and proliferation of hematopoietic lineages and also transduce a genuine lineage-determining signal in hematopoiesis.1 The future studies focusing on elucidation of the unique role of growth factors in a particular situation and/or microenvironment in various disease situations they may prove to be of critical clinical value.
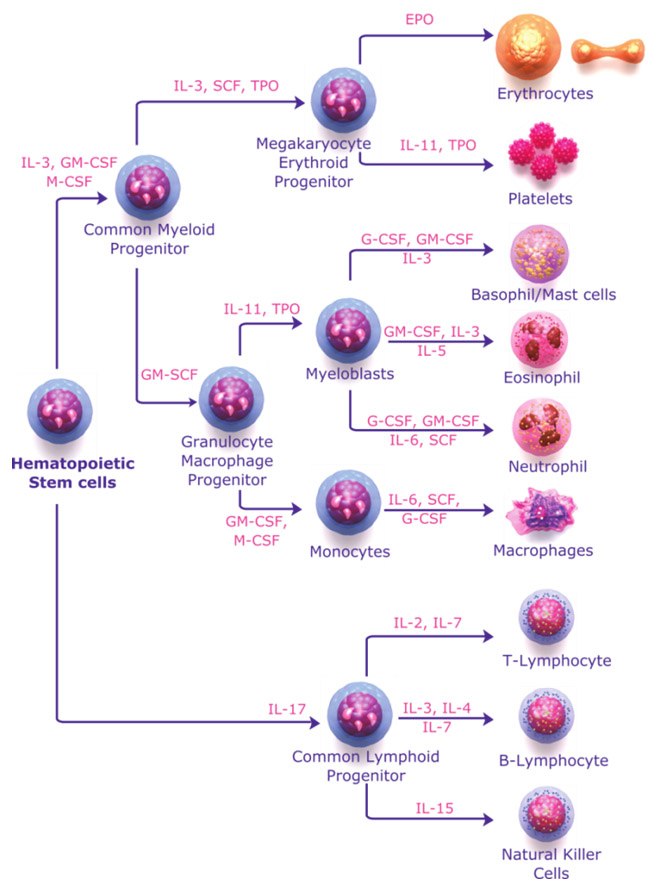
Figure 1.Hematopoietic cytokines stimulate hematopoietic cells to differentiate into principle types of blood cells.
Materials
Adapted from Hematopoietic Cytokines by Jennifer Fries, BioFiles 2009, 4.5, 8.
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?