Growth Factors and Cytokines
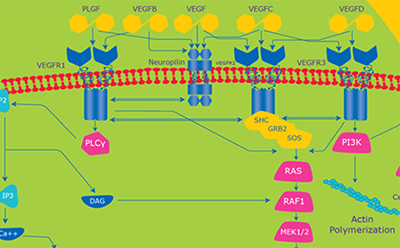
Cytokines and growth factors are chemical messengers that mediate intracellular communication to regulate cellular and nuclear functions. These soluble messengers bind cell surface receptors, which in turn initiate a transmembrane and intracellular cascade of events in the signal transduction process. Growth factor and cytokine receptors include many that are linked through G-proteins to membrane-bound phospholipase C (PLC) as well as protein tyrosine kinases (PTK). Activation of protein kinases catalyzes phosphorylation of other cellular proteins, which may orchestrate functional processes in the cell, or constitute one step in a protein kinase cascade that regulates nuclear events.
Not sure which growth factor or cytokine is right for your application? Check out our selection guide!
Products
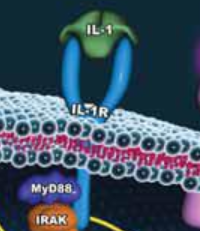
IL-1(interleukin-1) is one of many proinflammatory cytokines used in cell culture models
Growth factors are typically classified into ‘families’ according to factors like functional characteristics, or the cell types and cellular processes they regulate. For example, epidermal growth factors (EGF), generally affect epithelial cell types, while platelet derived growth factors (PDGF) act principally on fibroblasts commonly found in connective tissues. Cytokines, often compared with growth factors, are a pivotal part of the signaling mechanism that orchestrates the immune response. Beyond immune activity, cytokines may direct cell proliferation, chemotaxis, and even apoptosis. Cytokines and growth factors are somewhat similar in their structure and mechanism of action in that both bind to specific cell surface receptors, and that they bind receptors that share distinct structural homologies.
Other growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines have been associated with cellular defects and the pathogenesis of diseases, which is not surprising given their critical functions in a wide variety of biological processes. We offer several inhibitors, agonists and antagonists for target identification and validation in drug discovery. Explore our high-quality recombinant proteins for growth factor and cytokine studies to achieve consistent cell signaling outcomes.
Growth Factors and Their Receptors
Growth factors that activate tyrosine kinase receptors include epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibroblast growth factors (FGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), neurotrophins, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF). The receptor tyrosine kinases activated by these ligands include:
EGF Receptor (EGFR)
Members of the epidermal growth factor family (which includes Her-2/ErbB-2) have been associated with proliferation of tumor cells, enhanced tumor survival, angiogenesis, and metastatic spread.
FGF Receptors (FGFR)
The fibroblast growth factor signaling pathway is involved in embryonic cell proliferation, migration, differentiation and survival. In an adult organism, FGFRs function in tissue repair and response to injury.
PDGF Receptors (PDGFR)
Platelet-derived growth factor receptors activate various enzymes, transcription factors, and adaptor molecules. PDGFs have important roles in embryonic development, wound healing, and regulation of interstitial fluid pressure in tissues.
Trk
The tyrosine kinase family of cell surface proteins are tyrosine kinases that act as receptors for neurotrophins. Trks mediate neuronal survival, axon and dendritic growth, chemoattraction, and synaptic plasticity.
VEGF Receptors (VEGFR)
Members of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor family are specific tyrosine kinase receptors that are involved in mediation of blood vascular endothelial cell proliferation, angiogenesis, vasculogenesis, and embryonic organization of vasculature.
Cytokines
Like growth factors, cytokines are soluble signaling molecules that induce or regulate essential biological processes. Beyond their roles in pro- and anti-inflammatory induction, cytokines may regulate activation, differentiation, proliferation, or migration in immune and nonimmune cell types.
HumanKine® Growth Factors and Cytokines
We are proud to bring you HumanKine® growth factors and cytokines. These highly purified reagents are developed from an efficient human cell-based technology, and are excellent choices for your critical inflammation, cancer, stem cell, and antibody development research applications.
HumanKine® Growth Factors are:
- Produced in HEK 293 cells
- Recombinant and animal component-free for diverse applications
- Known to demonstrate authentic human glycosylation and post-translational modification patterns
Related Resources
- Article: Growth Factors and Cytokines for Cell Culture - Selection Guide
Learn more about the cell culture applications of growth factors and cytokines, including xeno-free and animal component-free products.
- Article: Growth Factors in Stem Cell Biology
Stem cell biology researchers use suitable growth factors to trigger proliferation, differentiation and/or migration of stem cells.
- Article: Hematopoietic Cytokines
Hematopoietic cytokines are large family of extracellular ligands that stimulate hematopoietic cells to differentiate into eight principle types of blood cells.
- Article: Interleukin Family (IL)
Interleukins, released from leukocytes, include IL-1β playing crucial roles in inflammation, immune responses, and anti-tumor immunity.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?