Primer Optimization Using Temperature Gradient
Optimization of qPCR Conditions
Optimization of qPCR conditions is important for the development of a robust assay. Indications of poor optimization are a lack of reproducibility between replicates as well as inefficient and insensitive assays. The two main approaches are optimization of primer concentration and/or annealing temperatures.
One approach to assay optimization is to determine the optimum annealing temperature (Ta) of the primers by testing identical reactions containing a fixed primer concentration, across a range of annealing temperatures. This can be achieved if a qPCR instrument with a temperature gradient block is available. In the format presented in this protocol, primers are included at a final concentration of 450 nM, and the gradient is orientated across the X axis of the block such that all columns are subjected to the same Ta (i.e., 12 different temperatures). In other instruments, the gradient is down the column such that all rows have the same Ta (i.e., 8 different temperatures). The following protocol can be applied to either, albeit after minor modifications.
Equipment
- Quantitative PCR instrument with integrated gradient block control function
- Laminar flow hood for PCR set up (optional)
Reagents
- cDNA diluted 1:5-1:10, gDNA 10ng, synthetic oligo (10,000 copies) or other suitable template for optimization.
- KiCqStart SYBR® Green ReadyMix™ (KCQS00/KCQS01/KCQS02/KCQS03; instrument specific, see Table P17-42).
- PCR grade water: PCR grade water (W1754 or W4502) as 20 mL aliquots; freeze; use a fresh aliquot for each reaction.
- Forward and reverse primers concentrated stocks (10 μM working stocks: GOI).
• Custom oligos can be ordered at sigmaaldrich.com/oligos.
Supplies
- Sterile filter pipette tips
- Sterile 1.5 mL screw-top microcentrifuge tubes (CLS430909)
- PCR tubes and plates, select one to match desired format:
• Individual thin-walled 200 μL PCR tubes (Z374873 or P3114)
• Plates
- 96-well plates (Z374903)
- 384-well plates (Z374911)
• Plate seals
- ThermalSeal RTS™ Sealing Films (Z734438)
- ThermalSeal RT2RR™ Film (Z722553)
Notes for this Protocol
- cDNA is generated using random priming or oligo-dT priming method and diluted 1:10 for use, but any suitable, alternative template may be used.
- All reactions are run in duplicate as technical replicates.
- If using a PCR plate, follow a plate schematic (e.g., shown in Figure P14-19) to ensure that the reaction mix, samples
and controls are added to the correct wells.
Method
1. Prepare a master mix for 56 reactions according to Table P14-35. Mix well, avoiding bubbles.
2. Remove 448 μL of master mix from step 1 (i.e., half ) into a separate tube for setting up the No Template Control (NTC)
reactions.
3. Add 112 μL of template to the remaining master mix from step 2. Set Template master mix on ice.
4. Add 112 μL of water to the other half of the master mix from step 2. Set NTC master mix on ice.
5. Aliquot 20 μL Template master mix from step 3 into two rows of the PCR plate labeled GOI.
6. Aliquot 20 μL NTC master mix from step 4 into two rows of the PCR plate labeled NTC.
7. Cover plates and label. (Make sure the labeling does not obscure instrument excitation/detection light path.)
8. Run samples according to the three-step protocol below
(Note: These conditions are specific for FAST cycling protocols) ensuring that the annealing temperature has been
defined on a gradient between the lowest and highest that would be appropriate for the primers (example shows
54–70 °C). Steps 1–3 are repeated through 40 cycles. A standard dissociation curve is run after amplification.
Note: Use standard dissociation curve protocol (data collection).
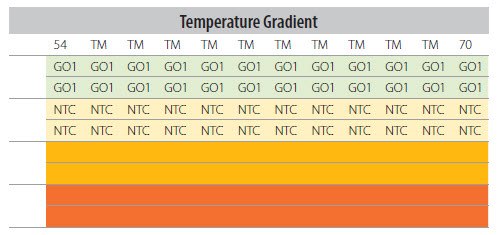
Figure P14-19. Plate Layout for Ta Optimization With Identical Ta for Each Column.
Note: The distribution of the samples and controls across the temperature gradient. If the instrument has a temperature gradient that varies vertically down the plate column, the samples and controls will need to be re-arranged accordingly.
Materials
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?