HPLC Determination of Vitamin A and E
Introduction
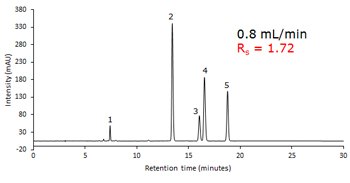
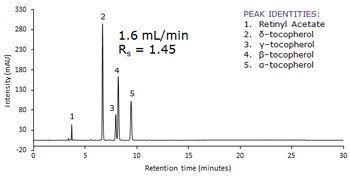
Following GB method for Vitamin A and Vitamin E as it is written with a 250 x 4.6 mm Ascentis® Express C30 column gives baseline resolution between the critical pair (gamma-, and beta-tocopherol; peaks 3 and 4). When a 150 x 4.6 mm Ascentis® Express C30 column is used, baseline resolution is still maintained with a separation that is complete in less than half of the time of the original method. Additionally, the flow rate can be doubled with the 250 x 4.6 mm Ascentis® Express C30 column, which gives a separation that is less than ten minutes compared to the original method. This application demonstrates how converting methods to superficially porous particle technology improves throughput.
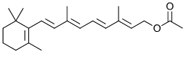
Vitamin A or retinyl acetate
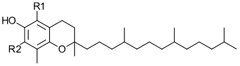
General structure of tocopherol
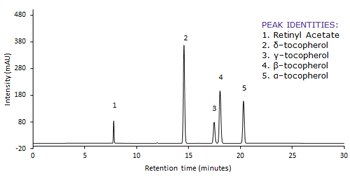
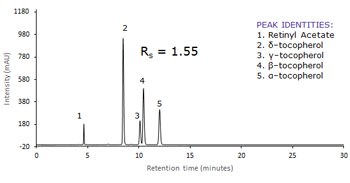
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?