Identification of Proteins in Lipofuscin Using Antibodies within the Human Protein Atlas
Background
The Human Protein Atlas (HPA) is a research project that aims to visualize the cellular and subcellular location of every human protein by using monospecific polyclonal antibodies1. This high-throughput approach enables the discovery of new protein distribution profiles and can also provide deeper insights into already known patterns. Here we used HPA antibodies to identify proteins associated with the age pigment lipofuscin.
Lipofuscin is mainly present in post mitotic cells. It consists of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and a small amount of metals. Despite that lipofuscin has been well-known for a long time the exact composition of the protein portion is uncertain2.
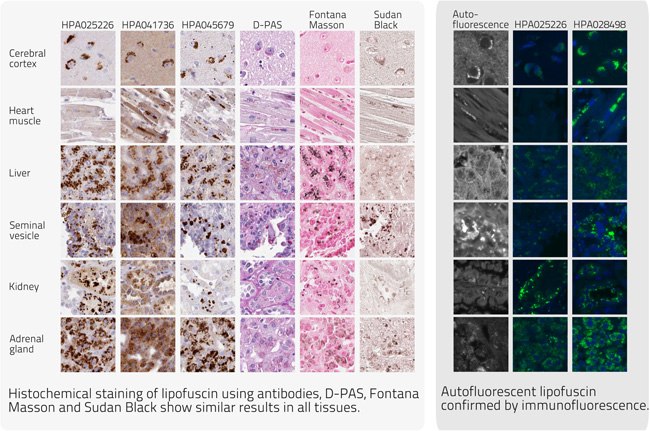
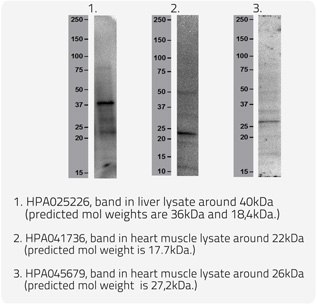
Conclusions
All methods; histochemical staining, confocal imaging and Western blot verified that the staining pattern observed by the antibodies was indeed lipofuscin.
The large collection of antibodies produced within the HPA project has proven to be a valuable tool to identify compartments of cellular complexes like lipofuscin.
A number of the previously unknown proteins within lipofuscin have been identified; GGH (HPA025226), MIP18 (HPA041736) and HDGL1 (HPA045679). Thereby a few pieces of the lipofuscin puzzle have been solved.
References
The HPR project is funded by the Knut & Alice Wallenberg foundation. The atlas is part of the HUPO Human Antibody Initiative (HAI).
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?