Phosphazene Bases
Introduction
Phosphazene bases are extremely strong and uncharged bases, built on a unit where a nitrogen basic center is double bonded to pentavalent phosphorus.1,2 Through oligomerization of the peralkylated triaminoiminophosphorane unit, the basicity improves dramatically (Figure 1). In the case of the monomeric phosphazene base, its basicity is about a 2-3 units beyond the basicity range of DBU (MeCNpKBH+ 24.3) and DBN, but reaches a MeCNpKBH+ of over 40 in the case of a tetrameric P4 phosphazene base (DBU = 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene, DBN = 1,5-Diazabicyclo- [4.3.0]non-5-ene).
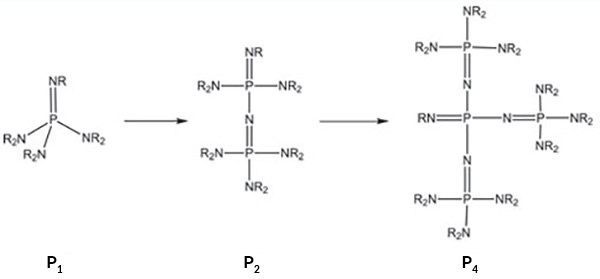
Figure 1.Monomeric (P1 and BEMP), dimeric (P2), and tetrameric (P4) bases.
We offer these reagents as monomeric (P1 and BEMP), dimeric (P2), and tetrameric (P4) bases with different side chains to control their sterical hindrance. Scheme 1 shows the basicity of phosphazene bases compared to other bases (in the absolute acetonitrile scale), as well as compared to the acidity of important organic compounds or classes of compounds.
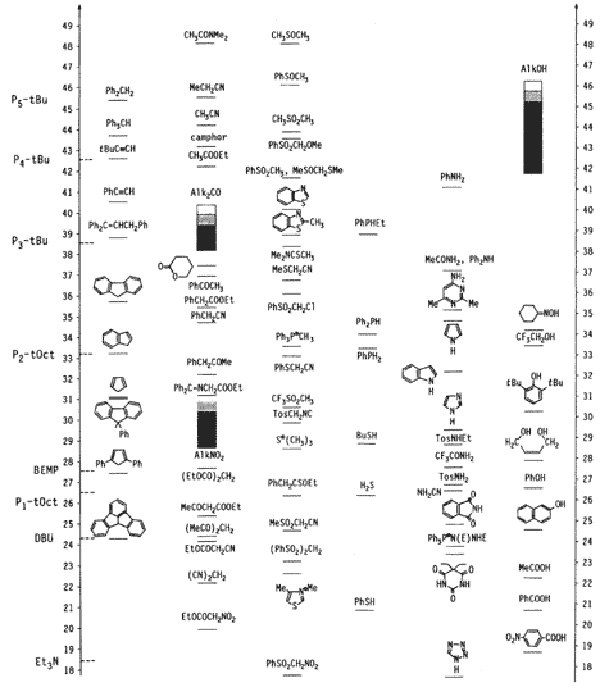
Scheme 1.
- Properties of Phosphazene Bases:
- High solubility in apolar to moderately polar solvents (e.g. hexane, toluene or THF)
- Very strong solubilizing effects in appropriate weakly acidic compounds
- Remarkably stable towards electrophilic attack, O2 and hydrolysis.
- Depending on their base strength, slightly to extremely hygroscopic
- Large sterical hindrance, depending on the type of side chain
- Applications of Phosphazene Bases:
- In situ generation of highly reactive "naked" anions, e.g. for alkylation reactions or for spectroscopic investigations.
- Applicable in reactions where ionic bases cause solubility problems.
- Applicable in reactions where ionic bases are sensitive towards oxidation or acylation.
- Applicable in reactions where ionic bases result in Lewis-acid catalyzed side reactions (e.g., in aldol reactions, epoxide-opening, hydride shifts, elimination of alkoxide, polyanion-formation).
- Benefits of using Phosphazene Bases:
- Easier work-up through cleaner reactions.
- Close to quantitative recovery.
- Reaction rate enhancement.
Phosphazene Bases Products
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?