Myelin Associated Glycoprotein (MAG)
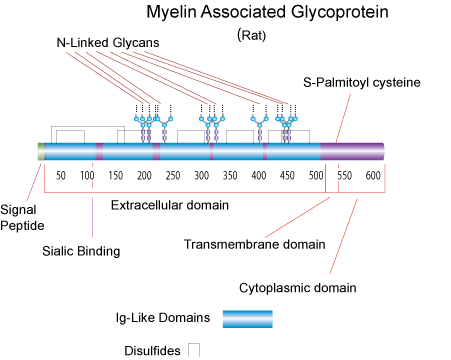
MAG is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein containing five Ig-like domains in its extracellular domain. It is an adhesion molecule belonging to the immunoglobin superfamily. These adhesion molecules bind specifically to cell-surface glycan containing sialic acid residues that define the I-type sialyl lectin subgroup. Thus, they are also called the sialoadhesin family. Sialoadhesins mediate diverse biological processes through recognition of specific sialyted glycans on the cell surface. MAG, a minor component of myelin in the central and peripheral nervous system, has been implicated in the formation and maintenance of myelin. MAG is expressed on myelinating oligodenrocytes and Schwann cells, and preferentially recognize a 2,3-linked sialic acid on O-linked glycans and gangliosides. MAG exists as two isoforms that differ in the sequence and length of the cytoplasmic tail. The large isoform (71 kDa) and small isoform (67 kDa) arise from alternative splicing of mRNAs. Lymphocytes under pathologic conditions, it would normally interact with neuronal cells. It has been shown that MAG promotes axonal growth from neonatal dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and embryonic spinal neurons, but is a potent inhibitor of axonal re-growth from adult DRG and postnatal cerebellar neurons. MAG plays an important role in the interaction between axons and myelin. A soluble form of MAG containing the extracellular domain is released from myelin in large quantities and identified in normal human tissues and in tissues from patients with neurological disorders. This soluble MAG may contribute to the lack of neuronal regeneration after injury.
| Myelin Associated Glycoprotein Products | back to Structural Proteins |
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?