Mucins, Glycosylated Proteins, Properties & Diagram
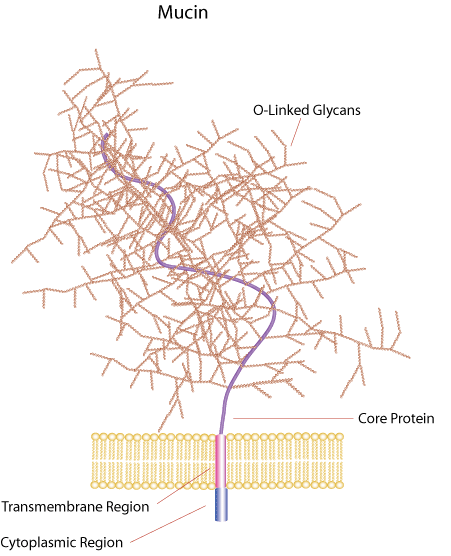
Mucins are a diverse family of densely glycosylated proteins. Mucin domains within the protein core are rich in threonine, serine and hydroxyproline enabling post-translational O-glycosylation. The highly glycosylated properties of mucins make them resistant to proteolysis and able to hold water, giving them the gel-like properties found in mucosal barriers. Mucins also contain cysteine-rich regions that participate in intermolecular cross-linking and are typically secreted as large aggregates. Mucins may also be associated with membranes and may serve as receptor-like ligands for carbohydrate-binding molecules.
Sign In To Continue
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?