Benzonase® Nuclease for Microbiome Workflows
Removal of host DNA is often necessary to lower the required sequencing depth, reduce cost, and improve the final data quality. Using Benzonase® Nuclease in a microbiome workflow reduces host DNA present in samples. Benzonase® Nuclease is a non-specific endonuclease that cleaves both RNA and DNA, which makes it effective at removal of exposed host DNA in microbial samples. The host DNA fraction of a microbial sample is easily exposed through osmotic lysis. This process takes advantage of the thick microbial cell wall, which prevents osmotic lysis of bacteria, even while the host cells are lysed. Benzonase® Nuclease then cleaves the exposed host DNA. Explore results from our team of experts with sample data showing how Benzonase® Nuclease reduces host DNA in Microbiome samples.
Benzonase® Nuclease for Reducing Host DNA in Microbiome Workflows and Enhancing Taxa Identification
This reduction in host DNA lowers the cost of sequencing by reducing the required sequencing depth and improving the quality of the resulting data. Microbiome saliva samples commonly have a high percentage of host DNA. The total DNA of a saliva sample consists of approximately 90% host DNA. This can be problematic for microbiome research as most of the sequencing reads align to the host organism. The consequence is that a much greater sequencing depth is required to capture all available microbial data, thus greatly increasing the cost of sequencing. Host DNA depletion methods resolve this issue by removing the host fraction of the DNA hence allowing greater resolution of the microbial fraction of a sample with a lower depth of sequencing and lower cost. Benzonase® Nuclease has been shown to eliminate free DNA from samples and can be used in host DNA depletion. Here we show that Benzonase® Nuclease effectively reduces the host DNA fraction of saliva samples and enhances microbiome DNA extraction methods.
Benzonase® Nuclease Sample Data and Methods
Saliva DNA extraction was performed on 6 fresh (not frozen) saliva samples with the MagMAXTM Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit. When using Benzonase® Nuclease, it is important to use fresh samples. Freezing and thawing cycles can lyse the bacteria, and the released bacterial DNA will be degraded by Benzonase® Nuclease. If using fresh samples is not an option, it is recommended to add a cryoprotectant medium such as 20% glycerol before freezing the samples to reduce the amount of cell lysis.
Half of the sample aliquots (“undepleted”) underwent the protocol as described by the manufacturer, while the other half of the sample aliquots (“Benzonase® Nuclease”) underwent an osmotic lysis in molecular grade water to lyse the mammalian cells, followed by treatment with Benzonase® Nuclease. The samples were pre-treated with Benzonase® Nuclease overnight to eliminate the exposed host DNA. Benzonase® Nuclease treatment eliminated most of the host DNA, reducing the host-aligned fraction from 87% in untreated samples to 30% in Benzonase® Nuclease treated samples (Figure 1).
Host DNA depletion using Benzonase® Nuclease for Microbiome Workflows
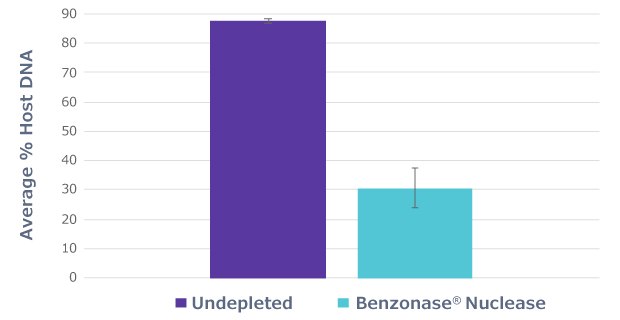
Figure 1.Benzonase® Nuclease incubation to deplete host DNA. Average percent host DNA identified by shallow shotgun sequencing of both Benzonase® Nuclease treated and untreated saliva samples shows that Benzonase® Nuclease eliminates the majority of host DNA.
Furthermore, taxonomic analysis of the samples shows an increased number of microbial taxa were identified in samples that underwent host DNA depletion with Benzonase® Nuclease (Figure 2). The removal of host DNA not only provided enhanced genus and species level identifications but also identified viral taxa that was previously missed in samples with a high fraction of host DNA. Overall, the data shows that depletion of host DNA with Benzonase® Nuclease prior to DNA extraction enhances microbial taxa identification while reducing sequencing costs.
Effect of Benzonase® Nuclease on Taxa Identified in Microbial Populations
Read Depth for Saliva Samples Host Depletion with Benzonase® Nuclease

Figure 2A. Benzonase® Nuclease increases the number of taxa identified in saliva treated samples. Sequencing Read Depth for treated and untreated samples, greater read depth was achieved for Benzonase® Nuclease treated samples.
Effect of Benzonase® Nuclease on Taxa Identified in Microbial Populations

Figure 2B.Taxa identified by bioinformatic analysis shows an increased number of taxa identified in samples treated with Benzonase® Nuclease to deplete host DNA.
Classification of a Representative Benzonase® Treated Sample
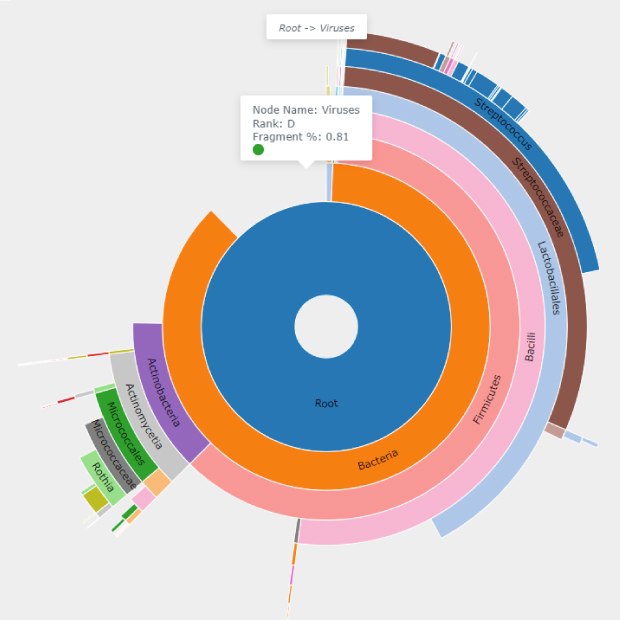
Figure 2C.Cake chart from the classification of a representative Benzonase® treated sample highlighting the viral domain, which was identified as 0.81% of the Benzonase® Nuclease treated sample. This domain was not identified in the untreated samples.
Benzonase® Nuclease Sample Data Methods
DNA Extraction
Using MagMAX Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit for Saliva from ThermoFisher and KingFisher instrument using the MagMAX_Ultra2_200uL_FLEX Protocol in a 96 well plate format.
Bacterial Lysis with Host Depletion using Benzonase® Nuclease
200μl aliquots of saliva sample combined with 15μl Benzonase® Nuclease (Millipore E1014-5KU) and 2mM Mg2+ and incubated at 37°C overnight. Proceeded with MagMax DNA extraction.
Library Preparation
Libraries prepared for shallow shotgun sequencing using NextFlex Rapid XP DNA-seq Kit from Perkin Elmer (Cat#: NOVA-5149-03). And NextFlex Unique Dual Index Barcodes from Perkin Elmer (Cat#: NOVA-514155). Final library concentration determined by Invitrogen Qubit, and final size determined by Agilent DNA 1000 Kit (Agilent, #5067-1504) on the Agilent Bioanalyzer.
Sequencing
The library pools were sequenced on the Illumina® MiSeq™ with a V2 reagent kit and MiSeq v2 500 cycle reagents by Our Microbiome Multi-Omics Services.
Bioinformatics Analysis
Classifications of the microbial composition was performed using our Bioinformatics Database and MCamp platform.
Materials
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?