Doyle Nickel Precatalyst Applications
Introduction
In modern transition metal-catalyzed coupling reactions, palladium has asserted its place as a dominant impetus. In comparison to previously used nickel catalysts, Pd(0) has been a proven precatalyst with diversity, accessibility, and robustness. However, Ni(0) has unique potential as it is more electropositive and smaller than palladium, facilitating oxidative addition. Along with that, it is smaller and significantly cheaper than palladium. Professor Abigail Doyle and coworkers have developed a compelling alternative to transition-metal catalysis with a nickel-based precatalyst.
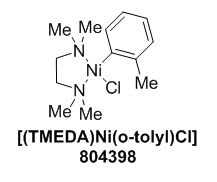
Ni(COD)2 is the most commonly used nickel precatalyst, but it is highly air-sensitive, necessitating the use of a glovebox. [(TMEDA)Ni(o-tolyl)Cl] (804398) is a versatile, air-stable nickel precatalyst that can be stored and weighed out on the bench.
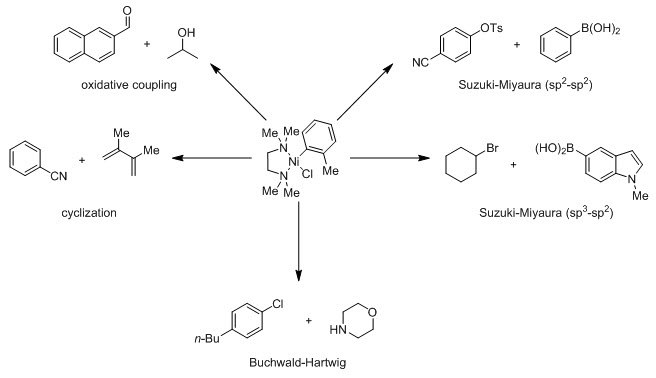
This precatalyst is competent for a wide variety of reactions, including Suzuki-Miyaura, Buchwald-Hartwig, Kumada, Negishi, Sonogashira, Heck, cyclization and oxidative coupling.1,2 This reactivity stems from the lability of TMEDA, which is readily displaced by mono- and bidentate phosphines, diimines, and N-heterocyclic carbenes.
Now making this revolutionary nickel precatalyst commercially available, in collaboration with Abby Doyle and coworkers.
For more on Abby Doyle’s Nickel-based transition-metal catalysis, visit her Professor Product Portal.
Special thanks to Mr. Jason Shields for contributing this technology spotlight.
Advantages
- Air-stable
- Modular
- Broad application
Materials
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?