UHPLC Vitamin D Analysis on Supel™ Carbon LC Columns
William L. Maule III , Clint Corman , Michael Ye , Cory Muraco , Curtis Frantz, Merck, Bellefonte, PA
Introduction
Analysis of vitamin D metabolites has continued to be a topic of interest in recent publications, primarily as biomarkers for possible disease states and vitamin deficiency. While vitamin D is present in two forms, vitamin D3 and vitamin D2, current ELISA methods demonstrate different cross-reactivities and cannot distinguish between D2 and D3 forms of the vitamin metabolites resulting in erroneous reporting of total 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. Further, there is interest in an analytical method to differentiate the D2 and D3 forms from the D2 and D3 epimers because of their different degrees of bioactivity. This application demonstrates the use of the Supel™ Carbon LC UHPLC column, with its ability to resolve structural isomers, to baseline separate all four analytes.
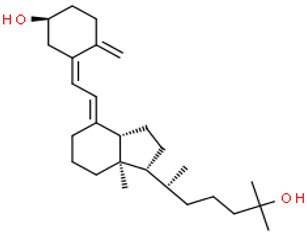
25-hydroxyvitamin D3
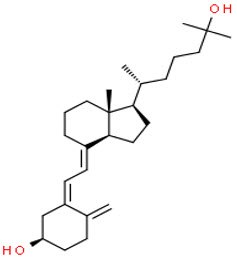
3-epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3
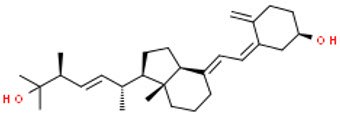
3-epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D2
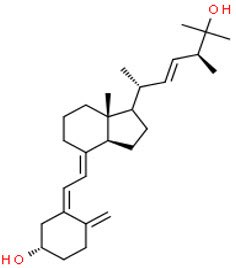
25-hydroxyvitamin D2
Chemical Structures of Vitamin D Metabolites
Experimental Conditions for vitamin D2 & D3 Metabolites Analysis
Performance Results
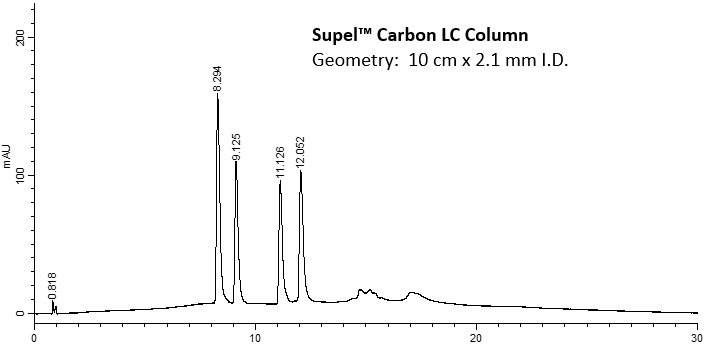
Figure 2.Analysis of Vitamin D Metabolites on Supel™ Carbon LC
Conclusion
This application has demonstrated the use of the Supel™ Carbon LC column to resolve vitamin D2 and D3 metabolites and their epimers. Baseline separation of all four analytes was achieved with excellent peak shape and sensitivity.
Materials
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?