Antibody Drug Conjugate Manufacturing
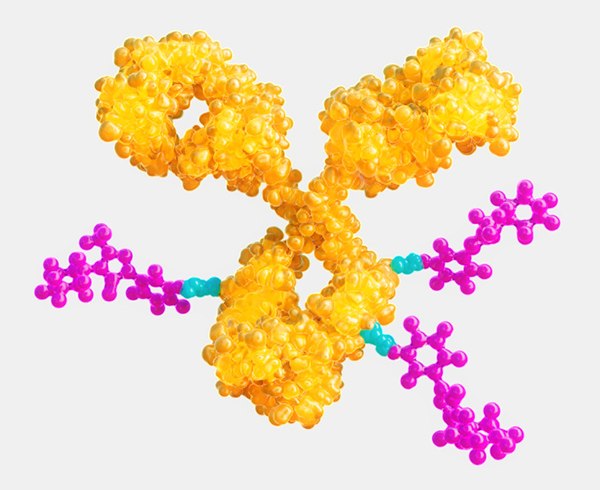
Antibody-drug conjugation (ADC) technology uses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to deliver potent, highly active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs) to targeted cells. In conjugated form, HPAPIs exhibit selective cytotoxicity which can spare non-target cells from toxic effects. Realizing the vast potential of ADC technology, however, is challenging and complex. Advanced manufacturing suites and dedicated equipment are necessary to characterize the molecule and demonstrate its purity, homogeneity, and stability. Efficiently linking a unique, tumor targeted mAb to a potent, cell-killing cytotoxic small molecule drug is only the beginning—meeting ADC manufacturing needs requires a comprehensive portfolio of products and wide-ranging expertise in small and large molecule development, manufacturing, and testing. |
Related Product Resources
Analytical Development and Product Characterization
Article: What makes a good ADC?
White Paper: Know your ADC’s Critical Quality Attributes
Webinar: The Benefits of Using Orthogonal Analytics in ADC Drug Development
Webinar: The Butterfly Effect: How to See the Impact of Small Changes to Your ADC
Webinar: Integrated Approach to Support ADC Programs From Concept to Clinical Material
Poster: Correlation of Discreet Drug-linker Variations on ADCs to Binding Activity
Antibody, Linker-Payload and Conjugation Services
Brochure: Discover Comprehensive ADC Services and Solutions
Webinar: Accelerated ADC Development with Integrated Supply Chain Solutions
Flyer: ADC Express™ Pre-clinical Conjugation Services for the Best Candidate Selection
White Paper: Commercializing Antibody-drug Conjugates: a CMO’s Journey
Linker-Payload Technology
White Paper: Benefits of Monodisperse and Activated PEGs in ADC Development
Flyer: Flyer: DM1 - Mertansine GMP Quality Payload For Your Drug Conjugate Programs
Flyer: Synthesise Dolastatin Payloads Faster and with Less Risk
Webinar: Payloads to Accelerate the Clinical Path
Processing Portfolio
Brochure: Biopharmaceutical and ADC Processing Portfolio
Biopharmaceutical and ADC Process Application Guide
Data Sheet: Eshmuno® CMX mix-mode chromatography resin
Webinar: Exploring enhanced selectivity of innovative ion exchange resin in ADC polishing
Single-use Template
Webinar: Tackling the Challenges of Single-use Manufacturing for ADCs
Case Study: Complete Single-use ADC technology, from development to scale-up
Application Note: Compatibility of a Mobius® Single-use Solution for ADC processing
Poster: Mobius® Single-use ADC Technology Supporting ADC Processing
Application Note: Pellicon® Capsules for Ultrafiltration/Diafiltration of ADCs
Webinar: Single-use TFF Capsules for mAb and ADC Processing
Keys to a Strong ADC PartnershipA seamless supply chain from gene sequence to stability testing of final drug product can reduce time to market by minimizing development and manufacturing complexity.
|
Workflow
Finding the Missing Link for Your Payload Supply
A highly active payload and drug-linker are matched with the mAb for eventual conjugation into an antibody drug.
Monodisperse and activated PEGs, or Chetosensar™ technology may solve solubility challenges during drug discovery and development. Advanced payload intermediates for the most common classes of payloads can help to reduce development timelines.
Connecting the Dots with Conjugation Services
The developed components of cell line, antibody, payload, and linker come together during conjugation and/or bioconjugation.
ADC Bulk Drug Substance (BDS) Testing Services
BDS as well as final drug product receive extensive analytical testing, including stability and release testing.
Conjugation with Cytotoxic Molecule
Linkage between the antibody and a highly active payload is a critical component of an ADC, requiring a broad range of products and chemicals.
Chromatography (Optional)
An optional chromatographic step can be used to remove high molecular weight species such as antibody aggregates and free drug residuals, while supporting optimization of drug-antibody-ratio (DAR) and control of polydispersity.
The Eshmuno® CMX resin has been designed for highly selective mixed mode chromatography.
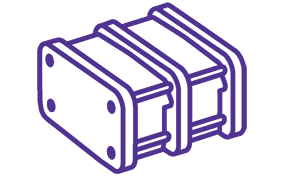
Ultrafiltration/Diafiltration
Removing residual solvent and free drug after conjugation is necessary prior to preparation of the final formulation with the desired concentration and buffer.
The Pellicon® Capsule is the first of its kind–a true single-use TFF device that comes ready to process ADCs in minutes.
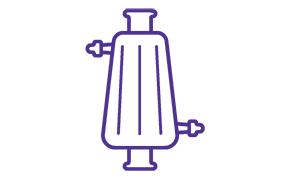
Sterile Filtration
Sterilizing-grade filtration is under increasingly intense scrutiny by regulatory bodies, requiring a high degree of sterility assurance.
Millipore Express® high area capsules and cartridges with SHC hydrophilic filters under Categories.
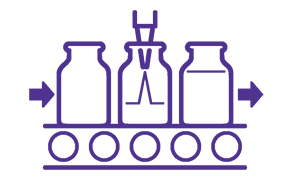
ADC BDS Final Fill and Formulation
The BDS is prepared for a final and unique formulation. The lyophilized dosage form is preferred and usually contains a buffer, stabilizer (e.g, trehalose or sucrose), and surfactant.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?